
Product Mechanism
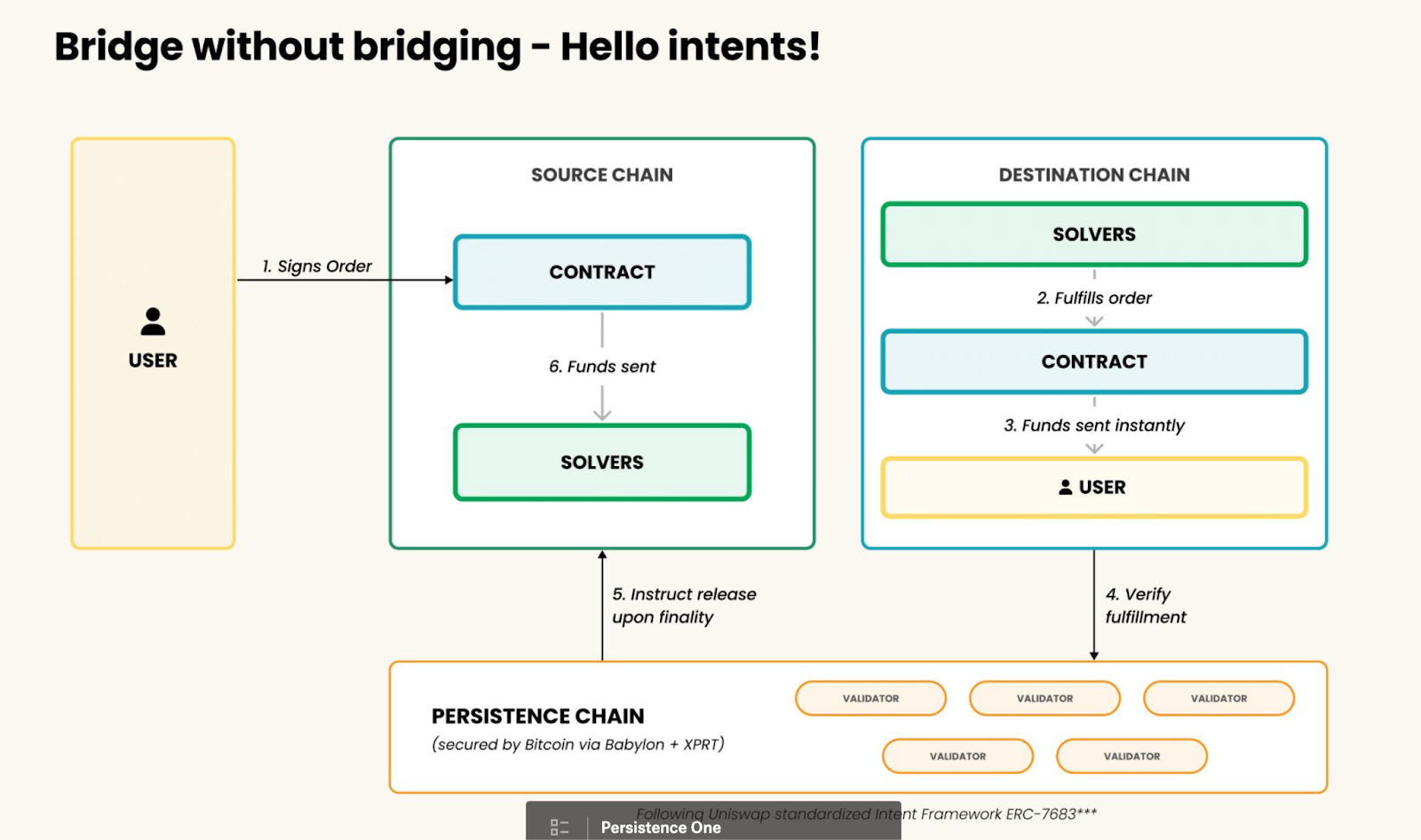
How Persistence One's Bitcoin Cross-Chain Swap Works
Persistence One is revolutionizing Bitcoin Layer 2 solutions and sidechains with its intent-based cross-chain swap mechanism. This innovative approach removes the limitations of traditional bridges, providing a seamless, secure, and efficient user experience.
Step 1: Submitting an Intent 📝
The process begins when a user wants to swap Bitcoin or any BTC-pegged asset across different Layer 2 networks. Instead of dealing with the complexities of traditional bridges, users can simply create an intent on the Persistence One platform.
- Users initiate the process by creating an intent on the Persistence One platform.
- An intent is a user-defined instruction specifying swap parameters such as the source chain, destination chain, asset type, and amount.
- Example: Swap cbBTC from Base to WBTC on the Bitlayer chain.
- The intent acts as a request for solvers in the Persistence network to fulfill, simplifying the process like placing an order.
Step 2: Solver Competition and Selection 🔍
Here’s where the real magic happens. Persistence One’s system leverages a decentralized solver network to efficiently fulfil user intents.
- Solvers are incentivized participants who monitor incoming intents and compete to fulfill them with the best possible rates, minimal fees, and zero slippage.
- These solvers can be professional market makers, LPs, or even programmatic bots.
- The competitive nature of solvers guarantees that users always get the best possible deal.
Step 3: Swap Execution and Settlement 🔄
The actual swap execution begins here. The entire process is designed to be trust-minimized, ensuring security and transparency.
- The solver facilitates the swap of assets between the source and destination chains, adhering to the predefined conditions set by the user in the intent.
- The system uses atomic swaps to ensure that assets are either swapped exactly as “intended”(based on user-defined parameters) or the entire transaction expires, eliminating any risk of partial fills or losses.
- If any transaction expires, the user has an option to reclaim its funds.
Step 4: Confirmation and Delivery ✅
After the intent is fulfilled, the user receives their assets on the destination chain, usually in seconds.
- Persistence One’s integration with LayerZero ensures real-time communication between the source and destination chains, allowing for quick confirmations and funds are released to the solvers on the source chain.
- Users can also track their swaps through the Persistence One dashboard, providing complete transparency.
Key Features and Advantages of Persistence One 🌟
🔒 Zero Slippage
By leveraging intents, Persistence One ensures that users are protected from slippage. The price is locked in as per the solver’s quote and user’s defined intent, so there are no unexpected losses.
⚡ Speed and Efficiency
Persistence One uses LayerZero’s messaging protocol to facilitate ultra-fast cross-chain communication, making swaps happen in seconds, rather than hours which is much faster than traditional bridges.
💸 Cost-Effective
By presenting the best quotes from the solvers, Persistence One offers lower fees compared to traditional bridges. Solvers are incentivized to provide the most efficient quotes, ensuring users get the best deal.
🌐 Scalability
The platform is designed to support swaps across multiple Bitcoin L2s, EVM-compatible chains, and non-EVM chains(soon), making it future-proof as the BTCfi ecosystem continues to grow.